The cost of data breaches is expected to rise from $3 trillion each year to more than $5 trillion in 2024, reveals "State of Cybersecurity Resilience 2021" report. That clearly explains the need for companies to have a well-grounded cybersecurity plan. While that stands true with all the companies across all industries, direct selling companies need to take extra care for safeguarding their business in the best interest of their customers.
Direct selling companies store prodigious amounts of personal information of customers, distributors, and employees. A lean security framework can prove fatal to the business. Today, 43% of cyber attacks target small businesses, especially those in the legal, insurance, retail, financial, and healthcare sectors. Businesses face cybersecurity accidents when they are least prepared for it. So having a foolproof security management plan in place is the ultimate weapon to defend the attackers before they even think of targeting you.


What is cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting assets that companies and individuals adopt to safeguard their critical systems and sensitive information from digital attacks. A strong cybersecurity architecture can safeguard digital assets and important personal and business information.
Before we draft a comprehensive cybersecurity plan, let’s outline the potential threats that could block the growth of your direct sales business.
The global cyber security market size was expected to reach $245.62 billion in 2024. The period 2025-2030 is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 12.9% to reach $500.70 billion by 2030.
Source: Fortune Business Insights
Types of cyber attacks that can hamper your direct selling business
In direct selling, rather than the financial information, attackers focus on the personal and behavioral information of individuals either to personally benefit from it or to make a fortune by selling it to the dark web where this information is used for malicious reasons unknown.
These cyber thugs unleash threats in a variety of ways making it hard for companies and individuals to defend themselves.
Malware attack
Otherwise called “malicious software” or “virus”, malware is a program built to automatically run unauthorized actions on the victim’s system. They attack your system creating malfunction and corrupting your hard drive or servers. It is typically delivered over a network or external devices connected to your system.
Ransomware attack
Ransomware is a form of malware that is sent to the target system either through email or other onsite or inapplication downloads. Ransomware holds the system hostage demanding ransom from the victim. Once the amount is paid, the attacker handovers the plan to revert the attack. These software files exploit system vulnerabilities that the company or individuals have not addressed. The fact of the matter is that no antivirus can safeguard or detect ransomware attacks.

Phishing
Phishing attacks are often done through email where the user is tricked into clicking a link that exposes your company information such as personal data, financial information, and passwords to the attackers. Phishing, being the most common type of attack, is involved in 36% of data breaches, according to Verizon's "2021 Data Breach Investigations" report.
Phishing appears in different forms often referred to as spear phishing or social engineering, whaling, and vishing. According to PurpleSec, 98% of cybercrime rely on social engineering to accomplish successfully.
Cross-site Scripting (XSS)
The attacker injects malicious scripts into websites viewed by victims. It is intended at gaining unauthorized access to data, accounts, or applications. Once the access is obtained the attacker gains complete control and can perform any action the user is authorized to do on the specific website or application.
DDoS attacks
Distributed Denial of Service attacks are targeted at your website denying users access to your services. It disrupts the normal functioning of your website with spam traffic flooding from multiple remote locations.
The frequency of DDoS attacks rose to 5.4 million in the first half of 2021 compared to the same period the previous year. In the fourth quarter of 2021, Cloudflare reported a 175% increase in the volume of ransom DDoS attacks compared to the third quarter.
While these are just the common types of attacks, these statistics provide a clear insight into the growing density of cyber attacks and the need to have an end-to-end security architecture in place.

"Most Firms still do not know where all of the sensitive information is nor what the criticality is, and we continue to see breaches because of it."
— Adrian Lane, CTO and Security Analyst
Developing a direct sales cybersecurity strategy
One study by the University of Maryland indicates that there is a cyber attempt every 39 seconds. Ever imagined the number of cyber attempts your businesses must be facing every day? Now that you know an antivirus or a PCI DSS compliance alone cannot meet your concern, you should be up for something more planned and strong.
A cyber attack can cost companies a great deal. A recent study by IBM’s security division revealed that data breaches now cost on average $4 million and the cost per record breached approximately amounts to $158. It is not just about the information being stolen but the legal and financial penalties that it would incur, the result would be devastating. Cybersecurity breaches also attack the brand trust built for years together. Both customer and distributor trust are built on how you safeguard their information and interests. Once that is broken that would literally be the end of your business.
Find out from our customers how our solutions give MLM businesses an edge and exceed customer expectations
A comprehensive cybersecurity coverage for your direct selling business
We have devised an 8-layered coverage plan to help you securely manage your direct selling business against challenges and threats, and safeguard your customer interests.
Detect system vulnerabilities
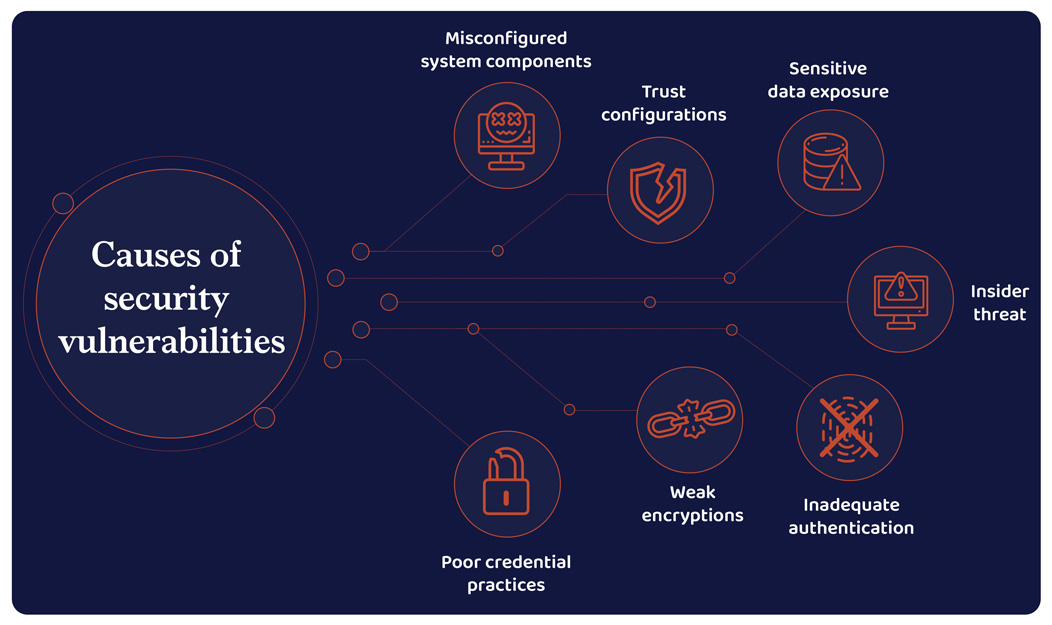
Unattended or unidentified security vulnerabilities lead to interrupted business processes adding to the damages caused to customer and distributor confidence and eventually to the organization’s reputation itself. What organizations must focus on is adopting immediate measures to limit the damage and weakness removed.
First and foremost, companies must have a blueprint on how vastly their data is spanned across the system. Always analyze and prioritize security risks. Constantly monitor your system for vulnerabilities with penetration tests and software audits. Identifying and fixing the issues on time can help mitigate the risk of being targeted.
Adopt a zero-trust framework
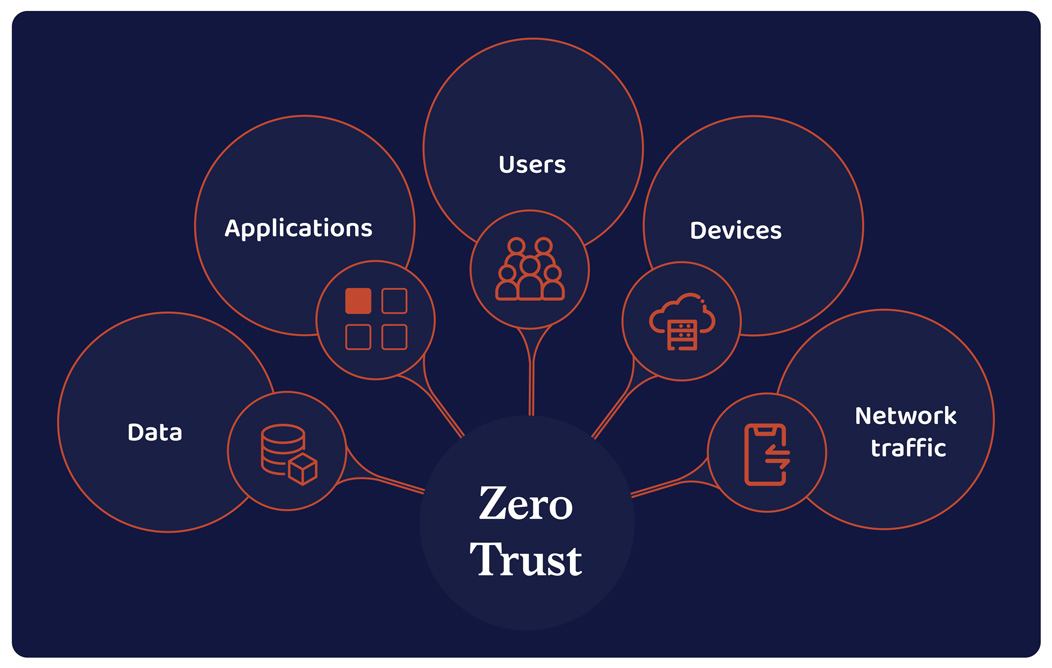
Ensure only the right people have access to the right resources. Secure everything from mobile devices to servers with authentication. In a study conducted by Microsoft, The Total Economic Impact™ of Zero Trust solutions, implementing a zero-security framework ensures a 50% lowered chance of data breach and over 50% improved security efficiency.
Build your zero-security architecture keeping your network, endpoints, data, and user account security levels in mind. Outline a strict user access policy to people across your organization.
Cyber insurance
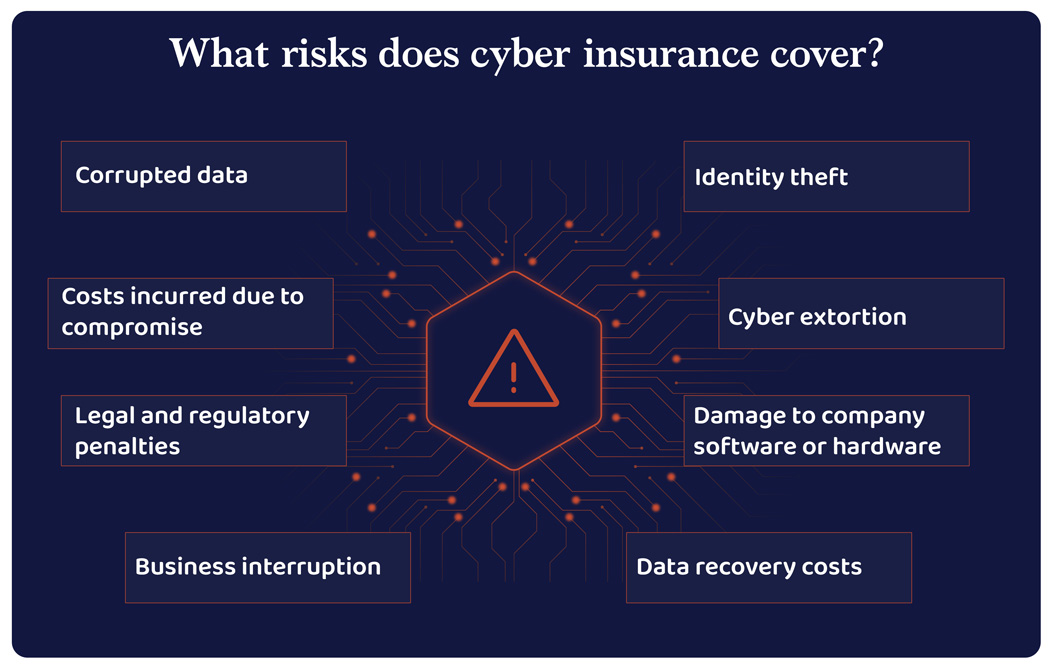
Cyber insurance gives you comprehensive coverage of your business liabilities including user information, social security numbers, credit card information, and health records against data breaches. Most cyber insurance policies cover data loss, cyber extortion, payment frauds, computer frauds, and loss of revenue due to breaches.
Cyber insurance supports the company’s commitment and responsibility to maintain steady compliance and regulatory standard in handling large amounts of user information.
Educate your people to detect potential threats
A large part of your organization is working remotely. Flexibility comes with an increased rate of risk associated with it. Distributors access your system from locations unknown and that increases your chances of being exposed to cyber attacks.
Conduct security awareness training programs and train them on the organization’s security protocol with mock threats and stealth tests. Implement periodic password changes and encourage them to use secure log-on processes.
Instill cybersecurity as a responsibility rather than an obligation.
Enable multi-factor authentication
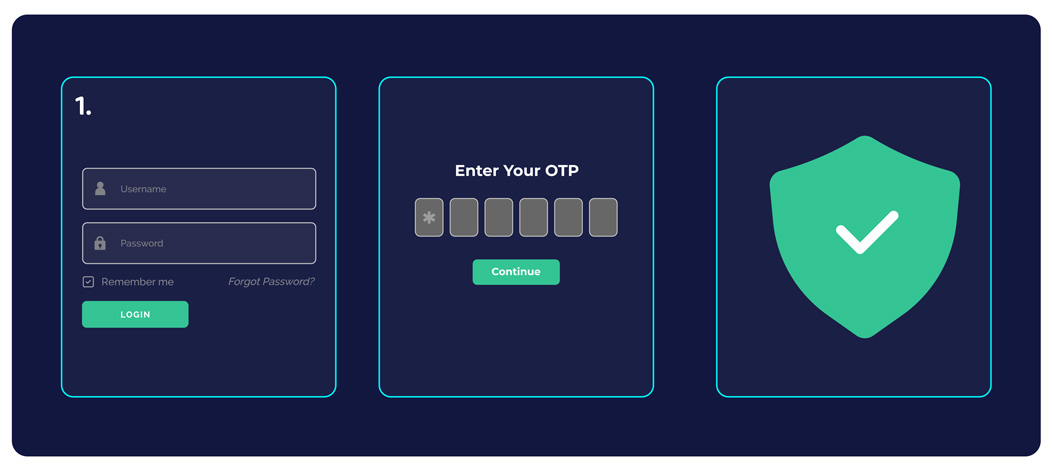
Multi-factor authentication is a foundational cyber defense mechanism in developing a strong cyber security plan. This enforces strict multi-layered authorization measures before granting access to systems or databases.
Multi-factor authentication should be implemented across all systems, networks, and applications across the organization. Identity and Access Management systems (IAMs) also act as an effective way for administrators to monitor and identify suspicious online activity in a cloud-based environment.
Perform penetration tests
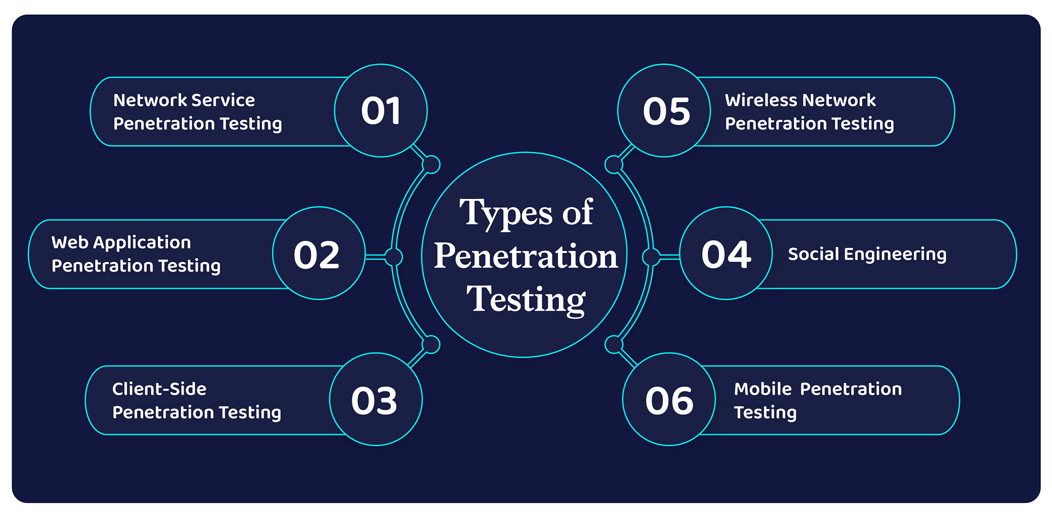
When cyber security challenges are growing in number, size, and forms, organizations are compelled to adopt a cybersecurity plan that helps defend themselves regardless of their size. Penetration testing becomes an integral part of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy for the fact that it helps organizations detect loopholes in their existing cybersecurity plan.
During penetration testing, mock attacks are performed to detect vulnerabilities caused by hardware or software design flaws, inefficient password management, or compromises made by human intervention. Penetration testing should be performed on all organization networks, applications, hardware, software, and user behavior.
Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence help companies leverage the power of data to make security-backed threat decisions and build effective defense mechanisms. This predictive capability helps identify attackers and respond faster to threat incidents. Threat intelligence is delivered through implementing the right tools, techniques, and procedures (TTPs).
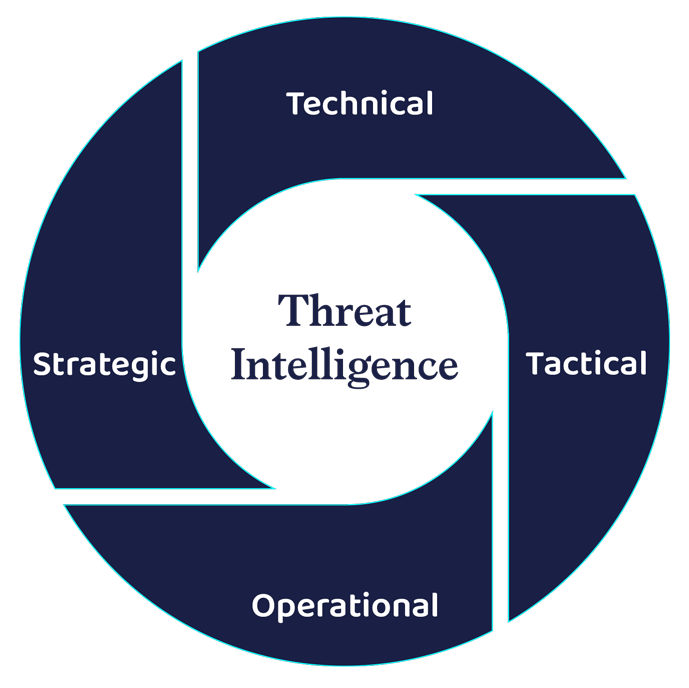
Threat intelligence is employed in 4 forms—tactical, technical, strategic, and operational. While tactical threat intelligence identifies simple indicators of compromises such as malicious IPs, URLs, or domain names, technical threat intelligence devises a defensive mechanism based on clues or evidence derived from previous attacks such as reported IP addresses, the content of phishing emails, malware samples, and fraudulent URLs, to identify the possibility of future attacks.
Both strategic and operational threat intelligence needs human intervention to be fully capable. Strategic threat intelligence delivers insights into the threats, preventive measures, and severity of the threats to the organization’s cybersecurity team. Operational intelligence analyzes the who, why, and how of attacks and provides organizations with a practical view of potential attacks.
Create a mobile incident response plan
Often overlooked, mobile devices also pose serious security issues for an organization. Mobile devices are more susceptible to data breaches and cyber threats. Hence including them in the cybersecurity architecture is of prime importance.
Companies must create an actionable incident response plan to safeguard the system before exploitation. As a first step to drafting an incident response plan, organizations must outline the scope of incidents and ways to detect and contain threats. A compact incident response plan must also outline methods to eliminate risks, restore systems, and constantly monitor to mitigate risks.
Consumer Sentinel Network, an investigative cyber tool by FTC, analyzed over 5.7 million reports in the year 2021 out of which 49% were fraud and 25% constituted identity theft. While both cases are serious causes for concern most companies back out considering the cost involved in implementing a strong cybersecurity architecture. If that is on your mind then what you should know is that a single attack of any kind, be it a data breach, malware, ransomware, or DDoS attack, costs companies of all sizes an average of $200,000, and many affected companies go out of business within six months of the attack, according to insurance company Hiscox.
So, what’s your cybersecurity plan?
Take control of your business security with an end-to-end security management framework.
Explore Now➔- What is cybersecurity?
- Types of cyber attacks
- Malware
- Ransomware
- Phishing
- Cross-site Scripting
- DDoS
- Direct sales cybersecurity plan
- Detect vulnerabilities
- Adopt a zero-trust framework
- Cyber insurance
- Threat awareness
- Multi-factor authentication
- Penetration testing
- Threat intelligence
- Incident response plan







Leave your comment
Fill up and remark your valuable comment.